Protocol Explained
A protocol is a set of rules that determines how data is sent and received over a network. It's like a language computers use to talk to each other, ensuring they understand and can respond to each other's messages correctly.
Key Elements of a Protocol
Types of Protocols
Network layer protocols operate in the network layer which is also known as the Layer 3 of the network architecture.
Transport layer protocols work in the transport layer which provides end-to-end service ensuring data transfer across apps on different devices.
Application layer protocol working in the application layer of the network architecture provides communication between applications running on different devices.
Wireless protocols basically used in wireless communication which enables data transfer through wireless networks.
Routing protocol establishes the best/optimal network pathways throughout the network for fastest data transmission.
Security protocol protects data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity while transmission of data over the network.
IP identifies devices uniquely. Internet protocol provides data communication through routing and forwarding data packets from one device to another by unique addressing scheme.
Important Protocols in Networking
Protocol Comparison Tool
Use our AI-powered tool to compare two protocols based on specific characteristics.
Protocols in Cyber Attacks
Attackers can misuse the rules of how data is sent over the internet to cause problems for systems.
For example, in a SYN flood attack, attackers exploit the TCP protocol. Normally, a device sends a SYN packet to a server to start a connection, and the server responds, expecting a final response to complete the connection. Attackers send many SYN packets but never respond, leaving the server waiting and using up its resources.
What Are Standards?
Standards are the set of rules for data communication that are needed for the exchange of information among devices. Many organizations are involved in setting standards for networking. The five most important organizations are:
Key Organizations
American National Standards Institute (ANSI)
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
World Wide Web Consortium (W3C)
Types of Standards
These are the standards that have not been approved by any Organization but have been adopted as Standards because of their widespread use.
Thus, these are the standards that have been approved by officially recognized bodies like ANSI, ISO, IEEE, etc.
Protocol and Standard Compliance
Interoperability
Protocols and standards allow diverse devices and systems from different vendors to communicate seamlessly and effectively.
Security Baseline
These established rules contain essential security principles and best practices that help create a secure network infrastructure.
Vulnerability Management
Compliance helps organizations methodically find and fix vulnerabilities, strengthening their overall security posture.
Best Practices for Compliance
Use cryptography tools to secure personal data transported across your network, making sure that data encryption methods exceed industry requirements.
Perform frequent security checks on all network devices to discover vulnerabilities and verify they fulfil compliance standards.
Restrict user access to specified network zones to ensure secure data sharing and prevent unauthorized access.
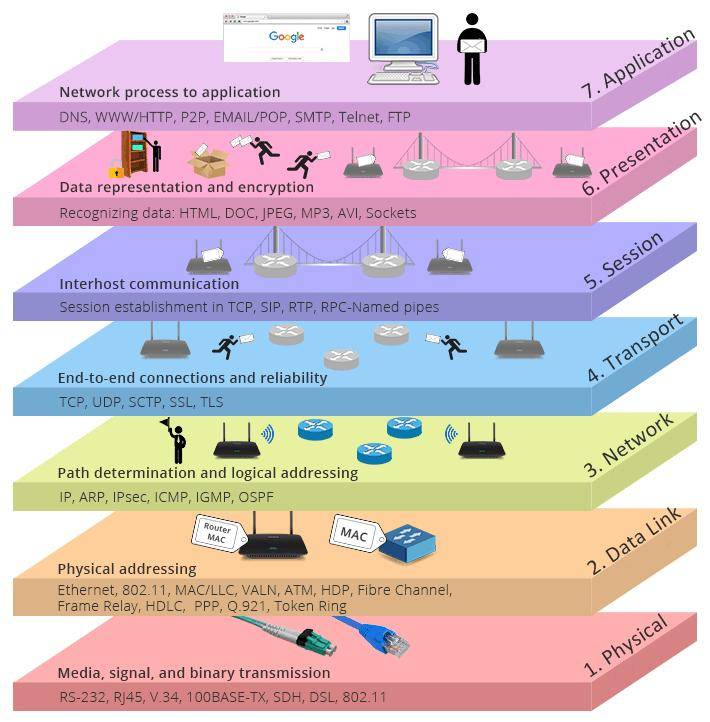
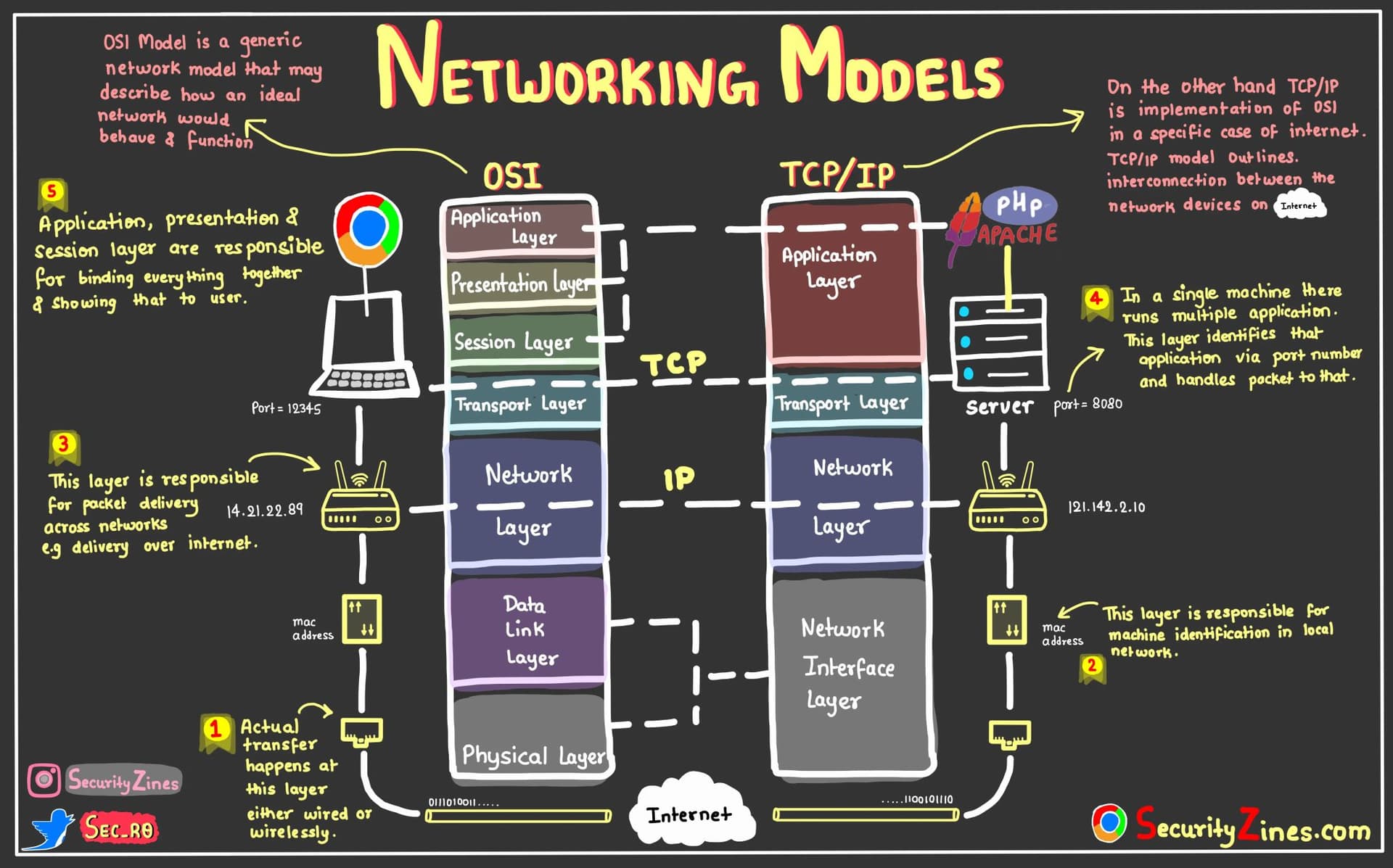
The Seven Layers of the OSI Reference Model
"OSI" stands for Open Systems Interconnection. The OSI model is a conceptual framework used to understand network interactions in seven layers, from physical connection to the end-user application.
Ready to Test Your Knowledge?
Take our quiz to see what you've learned.